What is Artificial Intelligence, and how can it help your company stand out?

You may already be seeing customised online ads, driving a Tesla or using Spotify's smart features to create personalised playlists. All of these are based on Artificial Intelligence!
It seems like this concept comes straight out of a sci-fi movie, but we are actually exposed to it every day. And it can even help your company boost its sales!
But what exactly is this 'artificial intelligence'? Well, that is a very good question! We will be happy to explain it to you below, but you can also learn much more about it in our new e-book entitled 'Artificial Intelligence: a powerful ally for your business'.
The e-book was written with input from our partner Trendskout, the Belgian authority on Machine Learning & AI-software.
What is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the umbrella term that refers to machines that exhibit 'human' behaviour. This includes the ability to reason, learn, schedule and even demonstrate creativity. In other words, artificial intelligence mimics human intelligence by displaying human-like skills.
The purpose of Artificial Intelligence is to relieve humans of their burden and to make them stronger. The fear that robots are made to 'take over the world' is therefore unfounded: AI is actually being used for our convenience.
Just as we solve mathematical problems with a calculator, we can tackle other problems using AI technology. After all, machines that can make decisions on their own for difficult problems thanks to AI applications can only be an advantage!
The question of whether or not a machine is intelligent (and therefore has AI) can be answered by taking the Turing test. The British mathematician and code breaker Alan Turing devised the test in 1936 to determine whether or not a machine can be considered intelligent and capable of thinking by itself.
In the Turing test, an interviewer chats with several contacts, one of which is a machine. If the interviewer cannot deduce from the answers provided by the machine that it is a machine that is chatting with him, the machine is said to exhibit intelligent behaviour.
Just think of a virtual assistant like Google Home or Apple's Siri: you can easily have a conversation with them – although machines are not (yet) very good at small talk. So you can usually unmask a machine if you use fillers like 'er', or start talking about your fun trip from last weekend!
The key elements of Artificial Intelligence
As we already mentioned above, artificial intelligence is an umbrella term that covers many different forms. Below, we will look at the two most important ones: Machine Learning and Deep Learning.
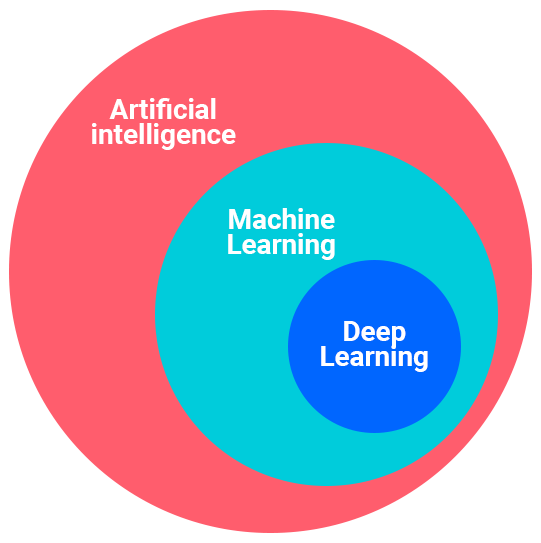
Machine Learning
Machine Learning is a subset of AI that focuses on methods that allow computers to learn from input data and patterns.
In practice, this is done using data mining. This is a technique for filtering relevant information from an enormous amount of data. A Machine Learning algorithm does not need structured data for this (such as an Excel file with neatly arranged data), as it is smart enough to decipher relevant data points from unstructured data.
This is also one of the reasons why the 'big data' phenomenon is becoming increasingly important for businesses: thanks to machines that use AI, the data can be processed more easily and put to good use.
Today, many companies have already adopted Machine Learning. Take bol.com, for example, which automatically recommends products to its users based on their previous purchases. Or Spotify, which creates playlists based on songs you have listened to before.
Deep Learning
Deep Learning (DL) is an advanced form of Machine Learning with only one big difference: self-adjustment.
In the case of Machine Learning, a machine can only adjust its behaviour through manual intervention (e.g. adapting the underlying code). A DL model, on the other hand, can adjust itself through external signals (data).
A perfect example is the AI technology used in self-driving cars. Such vehicles do not need explicit user feedback to adapt successfully. DL algorithms are primarily geared towards achieving the desired end result and making adjustments accordingly.
Practical applications of AI
Real-life application of AI in business
The number of applications of AI is almost endless. But in order not to dwell on the details, we will briefly look at how companies use AI in three different fields: Sales & Marketing, Manufacturing and Customer Service.
If you want to learn everything there is to know about all applications, please contact our partner Trendskout, the Belgian authority on AI software and Machine Learning.
1. Sales & Marketing
The need for AI software in Sales is quite obvious: salespeople are sitting on mountains of valuable data, but one of the biggest challenges is making sense of those massive amounts of data.
Even for the most experienced salespeople, it is almost impossible to extract all relevant information from the seemingly endless sales-related streams of digital information and then to interpret them correctly.
Fortunately, there is AI software that is usually easy to add to your current platform. This artificial intelligence can sift through large data sets and even make predictions about the future performance of your business. AI can thus help you learn quite accurately who will buy what, and when.
AI can also predict churn (i.e. the loss of customers) or help your sales force to make better decisions with 'next best actions' that can be used as a guide in conversations with a customer.

And, of course, AI can also help you with upselling and cross-selling. Because AI can interpret previous sales and make automatic decisions about what additional products or services an existing customer might need.
A company can have these suggestions automatically presented to the end customer or passed on to the relevant account or sales manager, depending on the business model of the company in question.
2. Manufacturing & Operations
AI can also work wonders in manufacturing facilities. For example, AI applications are able to predict the best time to maintain a particular machine, even before staff can do so, based on data science.
Of course, detecting anomalies in machines is something that has already been done before. But without AI, this was a very time-consuming and mostly error-prone manual process. Since the rise of AI and Deep Learning, the technology is powerful enough to detect all the nuances in the available data, and to take specific actions at an ideal time.
3. Customer service
AI in Customer Service – and by extension in all interaction with people – is based on NLP: Natural Language Processing.
NLP enables a computer programme to understand text or voice data and to respond to it with text or voice. The difference between this and a human response is barely noticeable. Ever had a chat with Google Home? You can, thanks to NLP!
But NLP is also extremely useful in the context of Customer Service. Because AI-driven customer service is able to identify frequently asked questions and provide satisfactory answers to them. The workload of the customer support staff is thus significantly reduced.
AI can also analyse 'customer service flows' and find out what the most frequently asked questions are, what answers are considered most accurate, and whether you can develop scripts for certain questions or touchpoints.
Gaining a competitive edge through AI
If your company focuses on innovation and adopts AI-based tools, it will have a huge advantage over its competitors. AI's computing power is invaluable and allows you to automate many business processes. This ensures efficient business operations, as well as a more satisfying user experience for your customers.
In this article, we briefly explained what AI is. In our e-book, you will find out even more about new products that can make your business systems more powerful.
